Synergy between human expertise and artificial intelligence for better oral health care.
Our research aims to harness the full potential of applied data science and artificial intelligence in dental medicine, advancing our understanding of disease and contributing to personalized treatment approaches.
Harvard course on AI in dental medicine
Co-chaired by Harvard School of Dental Medicine Dean William V. Giannobile and Balazs Feher, the first Harvard course on AI in dental medicine is designed to equip dental professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary to evaluate and effectively integrate AI-enabled technologies into their work.
Coming January 6, 2026 (Registration now open)
-
Comprehensive overview of AI in dentistry tailored to a clinical audience. 2 hours per week for 10 weeks; course meets weekly on Wednesdays 9–11 AM (ET).
-
Our course faculty bring broad experience in academic and clinical education, curriculum development, and faculty training. The course is made richer by the perspectives of distinguished guest faculty from institutions such as the University of Pennsylvania, as well as industry professionals at the forefront of translating AI into clinical practice.
-
Connect with dental professionals from around the world in lectures, interactive study sessions, small group discussions, and case studies. Course participants have exclusive access to a dedicated online platform to review and reflect on course material and network with like-minded global colleagues.
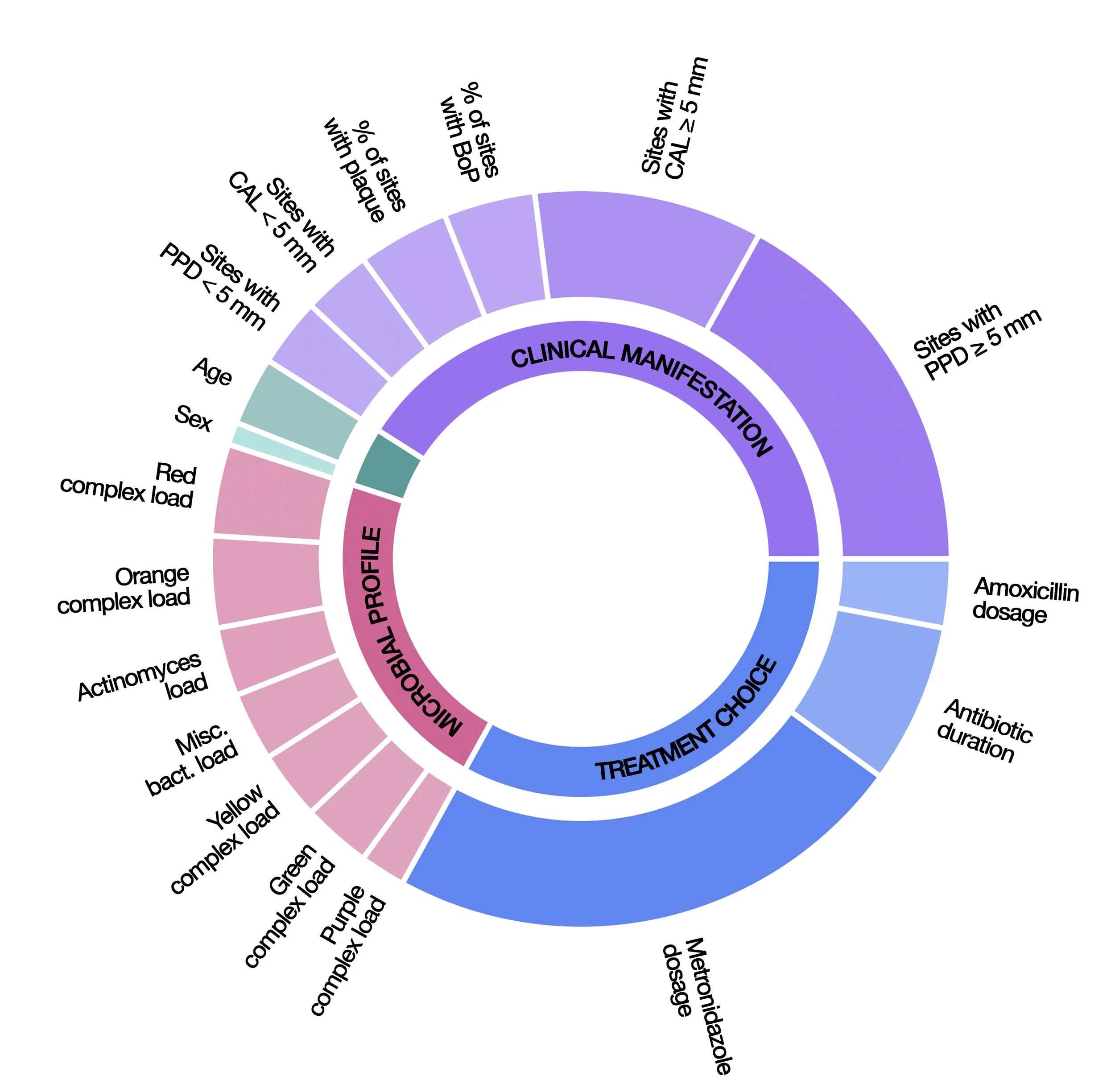
The first intercontinentally tested machine learning model that predicts individual responses to periodontal treatment.
Periodontal treatment is largely standardized, but individual outcomes can vary. Some patients experience disease progression despite adherence to treatment protocols. We developed a machine learning model to predict individual outcomes one year post-treatment using only baseline parameters. Our model was trained on South American patient data and tested on North American and European patient data.
A computer vision architecture that estimates periodontal stability at the tooth and patient level.
This work uses a combined object detection and image classification architecture on intraoral radiographs to estimate periodontal stability, which traditionally requires both clinical and radiographic examination, from radiographic signal alone. The model uses single tooth-level results to estimate periodontal stability at the patient level.
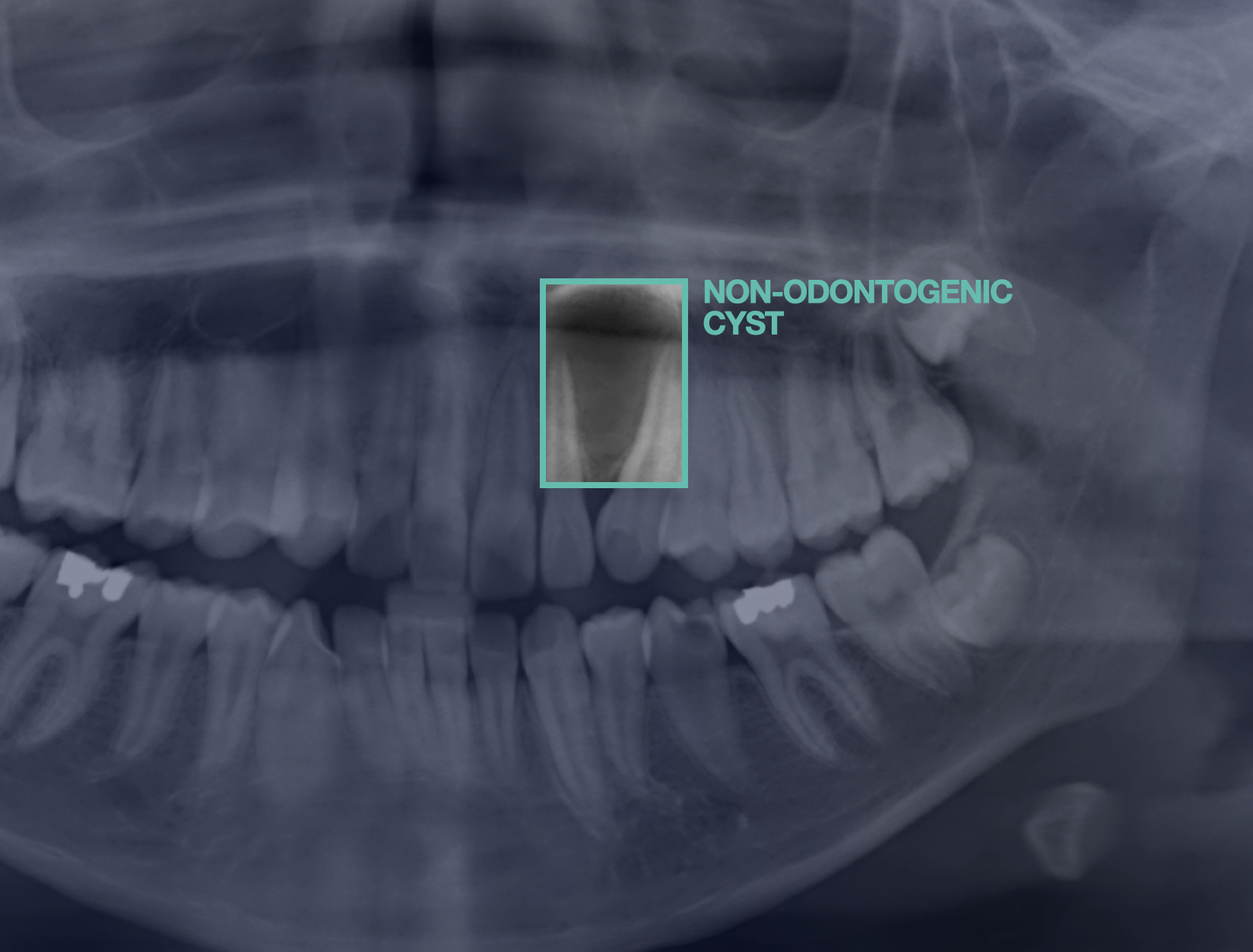
Machine learning models that diagnose jaw cysts and determine whether a tooth is involved.
In this international collaboration between twenty researchers from ten countries, we developed a machine learning workflow that diagnoses jaw cysts and classifies them into odontogenic (i.e., a tooth is involved) and non-odontogenic lesions, thereby aiding the surgical treatment planning process. The models achieved higher diagnostic performance than the international human control group.
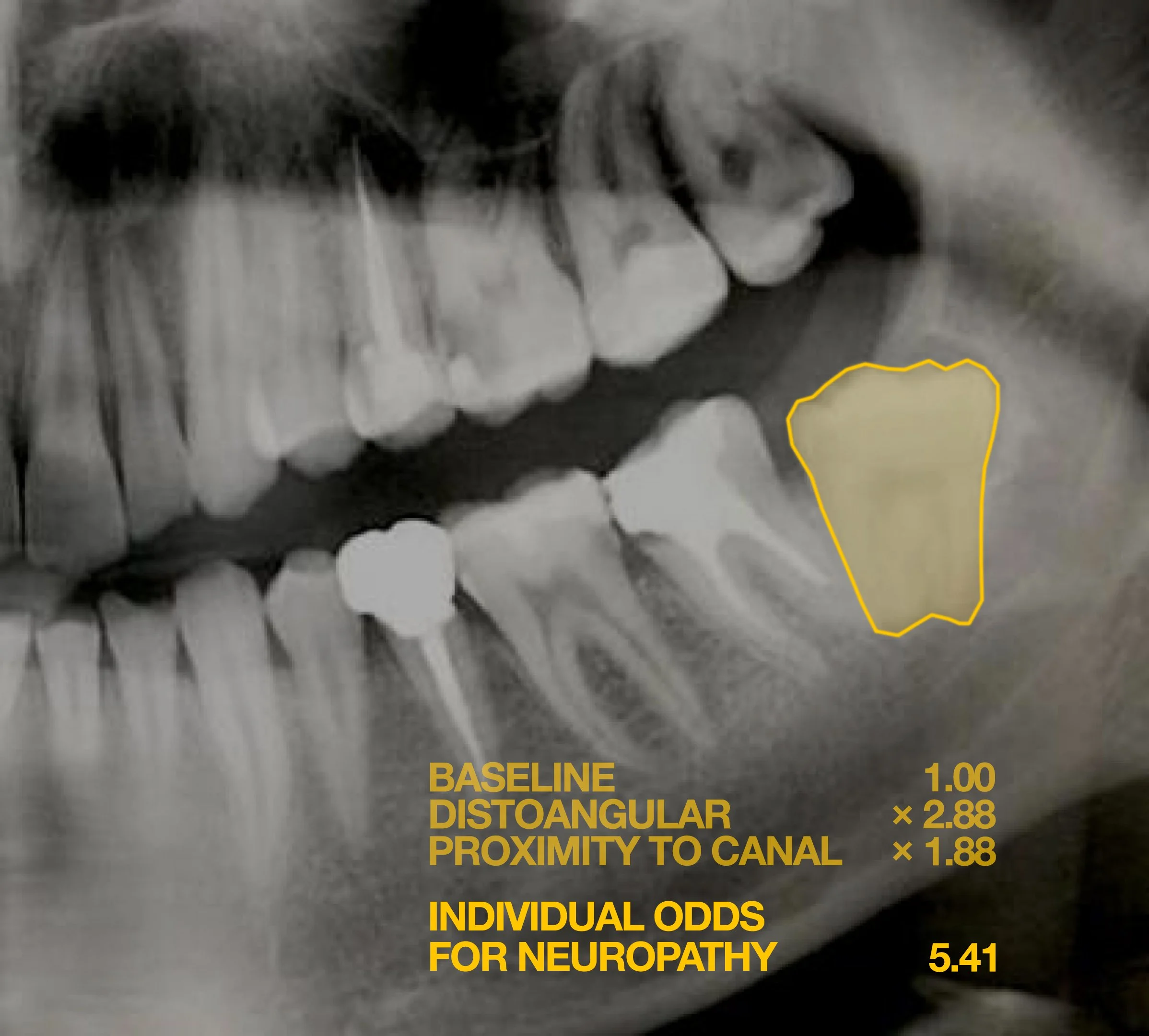
Predictive modeling that improves the outcomes of wisdom tooth surgery.
Postoperative neuropathy is one of the most severe complications of wisdom tooth removal, a routine procedure in oral surgery. In this work, we developed the first prediction model that not only uses advanced penalized regression to identify risk factors but provides individual odds that a given patient will experience postoperative neuropathy.

“Artificial intelligence holds enormous potential for improving the health of millions of people around the world”
WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus